Robotics in Manufacturing
The field of robotics in manufacturing has a bright future, from humanoid to industrial automation systems. While the demand for industrial robotics is constantly increasing, the challenges of adoption remain.
The adoption of industrial robotics typically faces three major obstacles:
- High investment costs and material constraints
- Long development cycles
- Limited data for testing and Machine Learning training
- Safety risks, for both material and operators
These constraints slow down innovation and can make for a tough barrier to entry to advanced robotics, especially to SMEs.
What is a digital twin?
Digital Twins address these challenges through high-fidelity virtual replicas of real robotic systems. By creating realistic simulations of complex environments, they enable engineers and researchers to test, train and iterate on their work before deploying anything in the real world, and to painlessly monitor and control installations already in place.
Through the AI-MATTERS project and the PRISM platform, CEA-List aims to create immersive digital twins that drastically reduce both time and costs by accurately mirroring complex robotics systems, at a fraction of their cost.
Overcoming constraints: Digital Twins as a catalyst for Data-Driven Robotics
Digital twins transform the robotics development pipeline by reducing the need for real world tests and therefore limiting expensive failures. They can also accelerate and improve testing, by running many more scenarios, more complex and diversified than possible in reality.
Additionally, they can present engineers with the possibility of generating as much data as necessary for AI training, benchmark, risk assessment or predictive maintenance. In that way, digital twins not only limit financial and time investments, they also unlock new horizons for industrial applications.
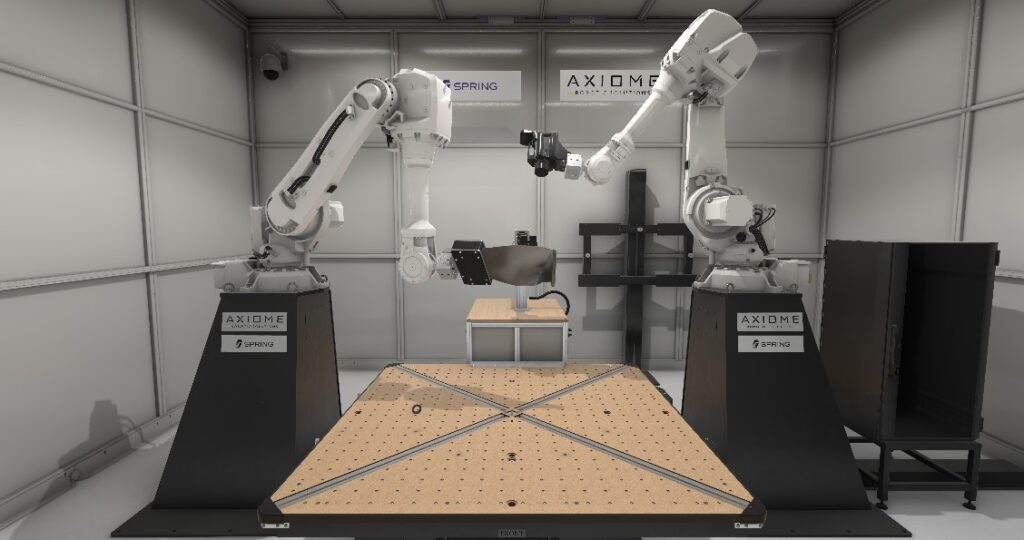
Digital Twin of SPRING, an integrated robotic cell for automated non-destructive testing
Projecting reality with accurate real time physics
At the core of our immersive digital twins stands XDE Physics, a real time physics engine developed at CEA-List specifically for robotics and manufacturing, with applications in the automotive, aeronautics, energy, and healthcare industries.
This engine is designed as an out-of-the-box solution that can be seamlessly integrated with mainstream 3D engines, such as Unity, Unreal Engine 5 and NVidia’s Omniverse, aiming to be as multiplatform as possible, and cover a wide variety of use cases.
Ce moteur est conçu comme une solution clé en main, pouvant être intégrée de manière fluide aux moteurs 3D grand public tels que Unity, Unreal Engine 5 et Omniverse de NVIDIA. Il vise à être le plus multiplateforme possible et à couvrir une large variété de cas d’usage.
Use cases
Factory digital twin for manufacturing & photorealistic 3D scans:
With digital twins being much faster, cheaper and easier to build than real factories, they can be used to predict performance, anticipate problems, and refine plans before materials are even bought.
As a proof of concept, we built a simplified model of a fully autonomous tricycle assembly line, in a demo allowing users to update it on the fly, both in Virtual Reality (VR) headsets and on their computer screen.
We also incorporated a 3D scan of the empty building into the digital twin, in order to preview the final look of the assembly line inside the building, all from a computer.
Simulation Unreal Engine 5
Simulation with environment scan
Reproduction of the PRISMA robotic work cell for additive manufacturing:
Even with existing infrastructure, digital twins are a powerful tool. As a practical example, we built a digital twin of PRISMA ; a robitic cell for additive manufacturing , to accurately model the trajectories of its robots in any given scenario.
With this simulation, we were able to create an efficient path planning application that limits the need for tests on the actual robots, reducing the time spent on testing from hours to minutes.
PRISMA robotic work cell
PRISMA digital twin
Unmanned drone digital twin for multi agent map exploration:
We have also used digital twins for larger-scale simulations. For instance, we use a digital twin of an unmanned drone as a platform to train machine learning algorithms that can be then transferred onto the actual drone to control it.
We also use the same platform to develop large-scale multi-agent simulations, where hundreds of drones can communicate and collaborate to complete complex tasks over vast terrains.
Digital twins are ideal tools for such projects, which would be unfeasible with real robots due to their impracticality and high cost.
Digital twin of mobile robot
Large-scale multi-agent simulation
Digital twins through the PRISM platform for innovation & robotics
Through PRISM, digital twins become more than simulation tools; they form a strategic foundation for scalable, safe, and data-driven robotics innovation. PRISM also contributes to digital continuity by bridging the gap between real robotic systems, their digital twins, and large-scale computing clusters, ensuring that data and models remain consistent throughout development, testing, and deployment.
PRISM is designed for both SMEs and large industrial groups, helping them plan, test, and train their systems before and after investing in expensive robotic equipment. Find out how AI-Matters can support your innovation process or contact us directly for a no-obligation conversation about the possibilities.
Find out how AI-MATTERS can support your innovation process, or contact us directly for a no-obligation discussion of possible opportunities.
👉 Contact our project managers for a no-obligations conversation about the possibilities
